Software testing is a crucial process within the software development lifecycle that involves evaluating and verifying a software application to ensure it functions as expected, meets specified requirements, and is free of defects. Its primary goal is to deliver high-quality, reliable, and user-friendly software by identifying and resolving issues before the product is released to users.
Key Aspects of Software Testing:
- Verification and Validation: Testing verifies that the software meets its design specifications and validates that it fulfills user needs and expectations.
- Defect Detection:It aims to uncover bugs, errors, and missing functionalities that could lead to system failures or poor user experience.
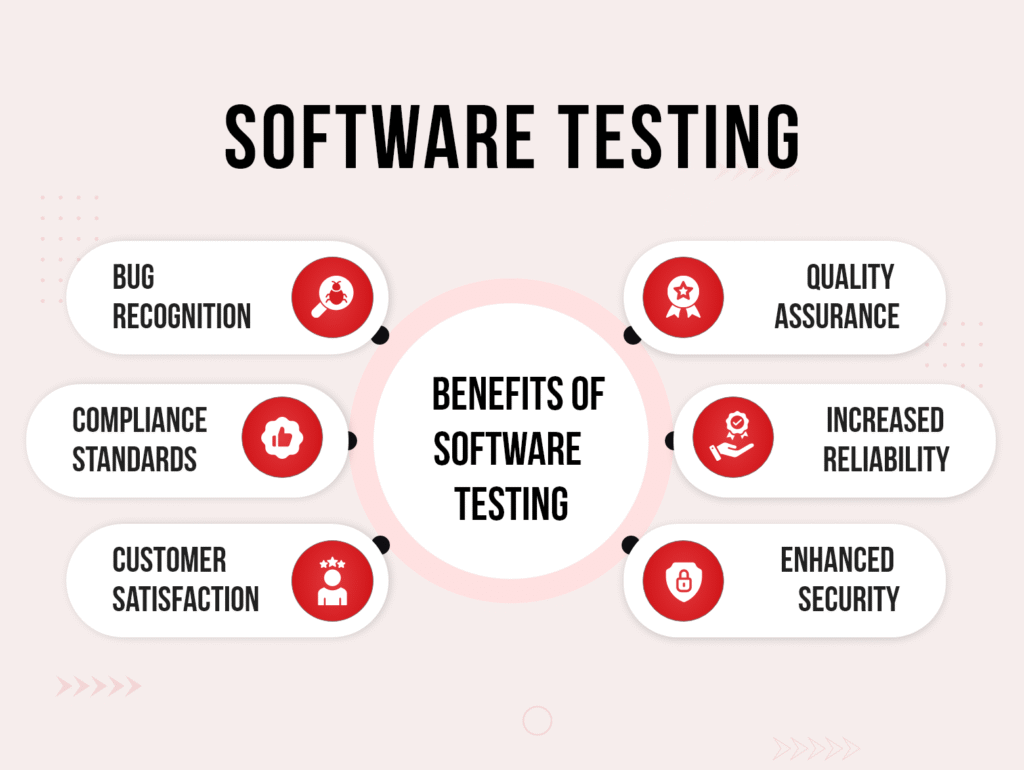
- Quality Assurance:Testing helps ensure the overall quality, performance, security, and usability of the software.
- Risk Mitigation:By identifying and resolving issues early in the development process, testing reduces the risk of costly fixes and negative impacts on user satisfaction after release.
Types of Software Testing:
Software testing encompasses various types, each focusing on different aspects of the application:
- Functional Testing:Evaluates specific functions and features of the software to ensure they work correctly (e.g., unit testing, integration testing, system testing, acceptance testing).
- Non-Functional Testing:Assesses non-functional attributes like performance, scalability, security, usability, and reliability.
- Manual Testing:Involves human testers manually executing test cases and observing the software’s behavior.
- Automated Testing:Utilizes tools and scripts to automatically run test cases, often used for repetitive tasks and regression testing.
Importance of Software Testing:
- Ensures Quality:Delivers a robust and reliable product to end-users.
- Reduces Costs:Identifies and resolves issues early, preventing more expensive fixes later in the development cycle or after release.
- Improves User Satisfaction:Provides a smooth and positive user experience by minimizing defects and enhancing usability.
- Enhances Security:Identifies and addresses vulnerabilities to protect user data and system integrity.
- Validates Requirements:Confirms that the software fulfills all specified requirements and business objectives.

Have a Project?
Are you planning a improvement in your business of your existing
product or planning to create a new project?
Say Hello! Contact us today.
